LEUKAEMIA Blood Cancer – A Silent Killer Disease
LEUKAEMIA Blood Cancer – A Silent Killer Disease – It is true that many of us do not know much about this sickness, leukaemia, maybe because it did not widespread like monkey-pox, Ebola virus disease, HIV/AIDS, Lassa fever etc. but it’s one of the most dangerous illness that has killed lots of people silently due to our negligence to it.
Contents
Leukaemia Blood Cancer Statistics
From observations and records, we found out that leukaemia disease was present in 2.3 million people and 353,500 persons died. It was also observed that about 90% of people with leukaemia are mostly adults.

This made people to be asking questions on what and way-about of this disease. People have been asking questions like; How would I know if I had leukaemia? How long does it last in the body? How rare is the disease? How long will my treatment last? What sort of treatment is needed for it? What should I avoid so that I won’t get the disease? What are the recommended foods to eat? And lots more.
Anyway, there is nothing to panic for as one thing is been said ‘once sickness is exposed, it really shows that it’s time to decamp or its expiry date is at hand.
Please feel free to read more about this illness/disease and also feel free to share with your friends and relatives as it will be better if we all join hands and tackle this together, for United we stand, divided we fall.
I know you will not like your friend or any of your family members to be a victim…
What is Leukaemia?
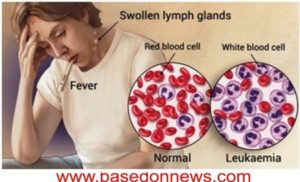
Leukaemia is a cancer that causes overproduction of abnormal white blood cells (lymphocytes) – a type of blood that defends the body against infection. So it starts from the bone marrow (blood-forming tissue).
The blood cells are formed in the spongy tissue found in the bones, simply put in the bone marrow. Stem cells or cells that have not matured which become matured blood cells over time are produced during the division of blood forming stem cells.
We have two major groups of blood stem cell, which include myeloid stem cell and a lymphoid stem cell.
A myeloid cell can easily become any of these matured blood cells such as; red blood cells (a cell that carried oxygen round the body), Platelets (stops bleeding through formation of blood clots), Granulocytes (white blood cells that fight against disease and infection).
If the blood stem cells divides to a lymphoid stem cell, it could easily become; B lymphocytes (it produces antibodies that helps to fight against diseases and infection), T lymphocytes (it helps B lymphocytes in making antibodies to fight against diseases and infection) or NATURAL KILLER CELLS (IT ATTACKS CANCER CELLS AND VIRUSES).
Therefore, Leukaemia is a blood cancer that affects the white blood cells either myeloid stem cell or the lymphatic stem cell and from there the sickness continues.
TYPES OF LEUKAEMIA
We have about four major types of leukaemia:
- Acute lyphocytic leukaemia (ALL): This is the type of leukaemia that affects lymphocytes. It develops rapidly. It is caused by the accumulation of cancerous lymphoid cells like B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. It can be cured with standard treatments such as bone marrow transplants
- Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL): This type of leukaemia also affects lymphocytes but it develops slowly. It cannot be treated with standard treatments but it can be treated and managed.
- Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML): This type of leukaemia affects myeloid cells. It develops rapidly. It is caused by the accumulation of cancerous myeloid cells in the stem cells.
- Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML): This is the type of leukaemia that develops slowly and also affects myeloid cells.
Note: Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) and Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) are mostly common among adults while Acute lyphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) are common among the children.
In recap, leukaemia is more common in adults than in children.
CAUSES OF LEUKAEMIA
Before I will move deep to the causes of leukaemia, I will like to spell out vital points here.
Always remember that leukaemia is not inherited (that is passed from parents to their offsprings), it is not also a sickness that is contagious (that is communicable – transferred from one person to another).
Now the causes include the following:
- Genetics condition: There is indeed higher chance that relatives of patients of leukaemia may develop some forms of leukaemia. It is demonstrated by family history whereby the affected people may have in common a single gene or multiple genes, thereby developing same kinds of leukaemia as other members.
- High exposure to chemicals: This is as a result of being exposed to some chemicals such as benzene, and viruses such as the Human T-Cell leukaemia virus, may increase the chance of developing leukaemia.
- Radiation: Being exposed to high levels of radiation may increase the chance of developing leukaemia. As the emission from nuclear reactors mostly called bone seeker increases leukaemia in animals and bone cancer, it is also assumed that it may do so in human beings.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF LEUKAEMIA
The signs and symptoms of leukaemia arise when the bone marrow is full of leukaemia and is unable to produce a good number of normal blood cells which the body needs. Once this happens it will lead to:
- Tiredness/weakness, shortness of breath, light-headedness, palpitations, weight loss
- Anaemia as a result of insufficient red blood cells/erythrocytes
- Infections due to lack of white blood cells/lymphocytes
- Small bruises in skin, nosebleeds, heavy periods, bleeding gums
- Lack of platelets which results to lack of platelets
- Fever, always feeling of illness, sweats
Note: Children with Acute Lymphotic Leukaemia (ALL) always complain of pains in their bones or joints.
HOW LEUKAEMIA AFFECTS THE BODY
Leukaemia can affect the body in so-many ways, mostly, Acute leukaemia results when abnormal white blood cells/lymphocytes increases rapidly and flows into the blood stream. Then, when it’s not treated, the leukaemia cells crowds and push out the healthy cells making the body to be starved of oxygen, thereby little or no immunity to disease is left.
Also chronic leukaemia occurs when the blood stream or bone marrow is filled with abnormal white blood cells that refuse to die
HOW LEUKAEMIA IS TREATED
The possible ways to treat leukaemia include:
- Biological technique: This is the treatment with the use of immune system to destroy leukaemia cells.
- Stem cell transplant: This is a situation whereby a donor donates a stem cell for a stem cell transplant or bone marrow transplant to a patient
- Chemotherapy: This is a cell-killing drug for leukaemia and other related diseases
- Targeted therapy: This is the use of recommended drugs to kill leukaemia cells
LIKE our Facebook page for more updates. Comment below to encourage us more
